SUMMARY OF RANSOMWARE THREAT ACTOR ACTIVITY IN 2023 (ENG)
Introduction
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data on the targeted system and demands a ransom payment from the victim in order to restore the system and decrypt the data.
In this report, the Threat Research Lab at NSHC has described the results of analyzing hacking activities by hacking groups using ransomware that occurred during the year 2023. It also includes an analysis of the attack techniques, tools, and infrastructure used by these hacking groups during their hacking process.
Monthly Ransomware Hacking Activities
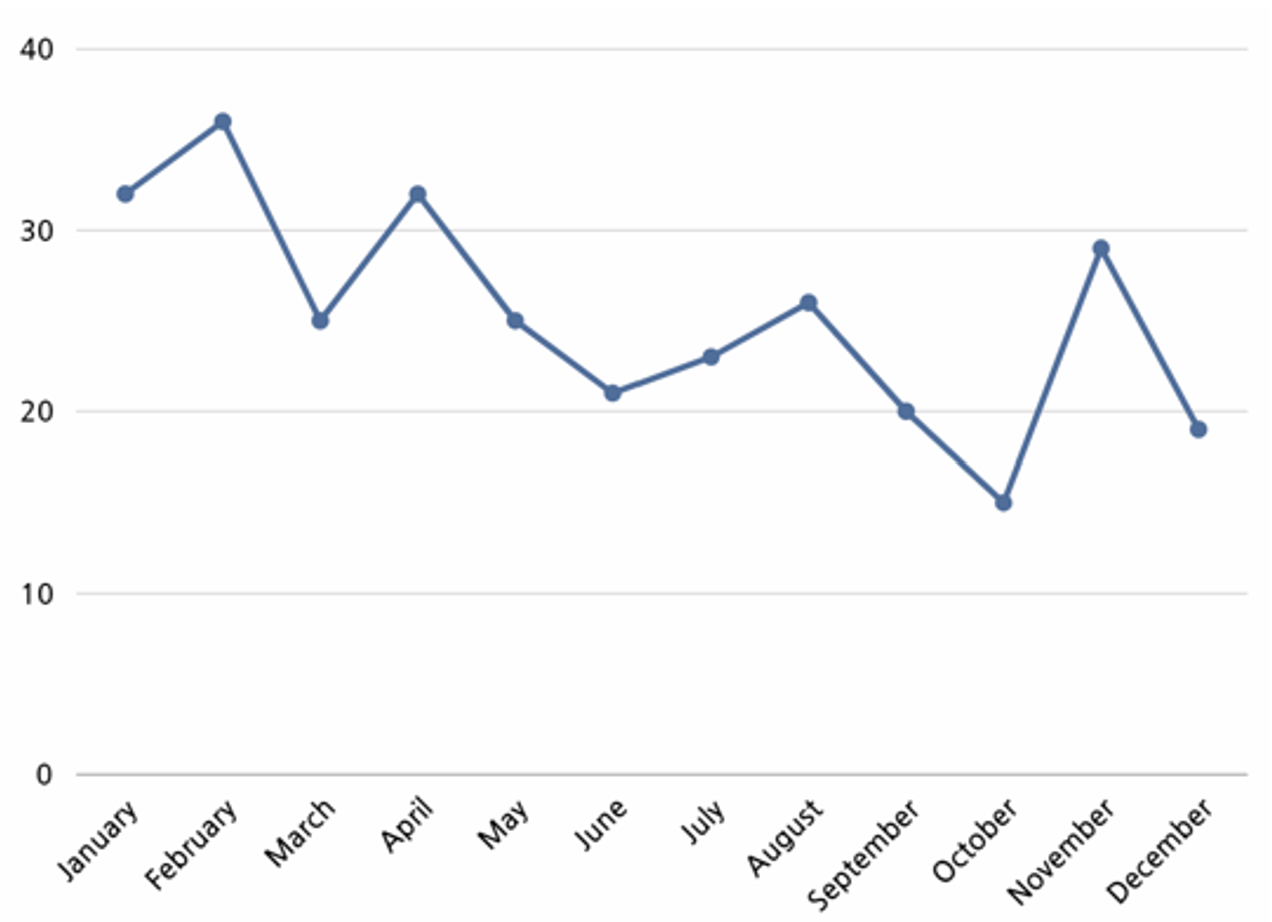
In 2023, a total of 304 threat events related to hacking activities by hacking groups using ransomware were identified from the Threat Analysis Research Institute.
Analysis of the threat event status shows that most events occurred in February for the first half of 2023, and in November in the second half of the year.
[Figure 1: Statistics of hacking events using ransomware by hacking groups in 2023]
The reason behind the high number of events in February accounts to the fact that the hacking groups attempt to exploit new security vulnerabilities that were identified at the start of the year, and security checks are conducted less often in comparison to the end of the year.
The high number of events in November is due to the attempts to maximize financial gain by targeting companies and institutions during large-scale shopping seasons such as Black Friday.
From the statistics, it could be seen that an average of 25 ransomware attacks occur per month. Although a decreasing trend in the number of ransomware attack is observed, there are points where attacks suddenly become active again, indicating that ransomware attacks occur continuously.
Format of Ransomware Hacking Activities
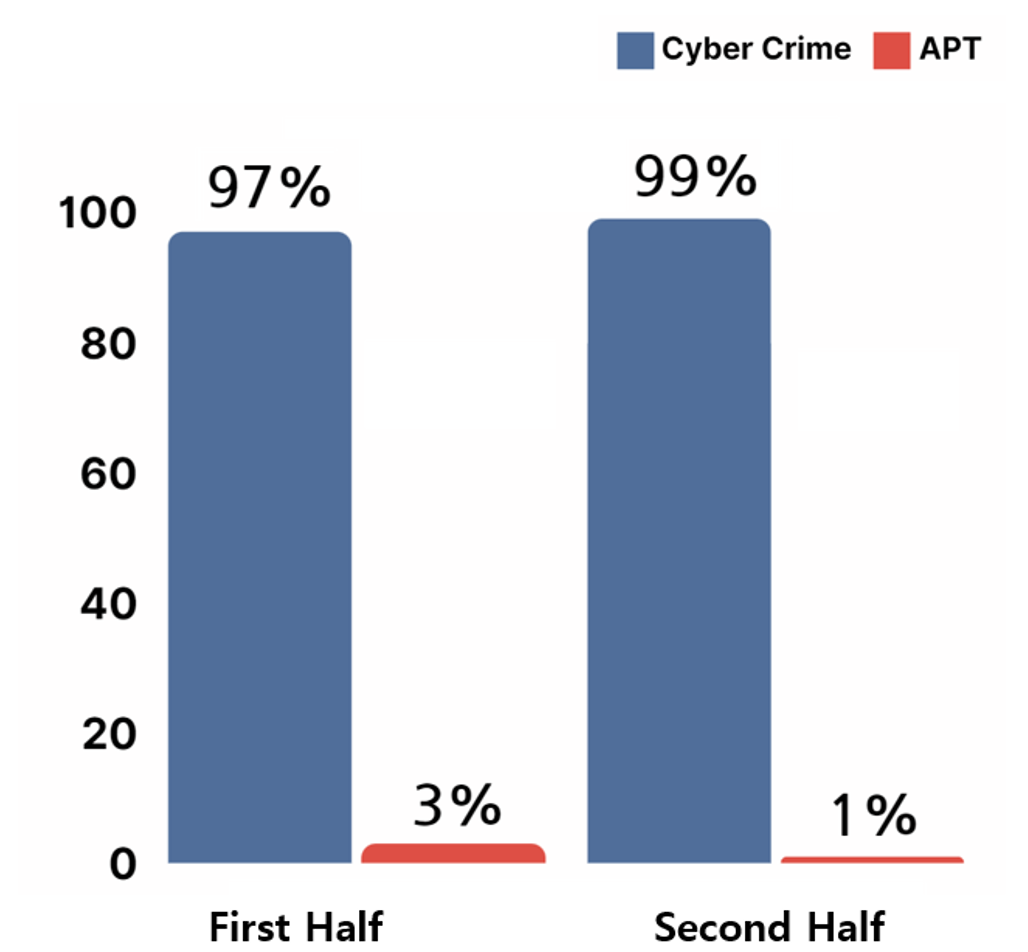
The entities behind ransomware hacking activities could be classified into two groups, either the cybercrime groups that carry out hacking activities with the aim of securing financial profits, or APT groups that receive support from governments.
Analysis of ransomware hacking activities in the year 2023 showed that cybercrime hacking groups made use of ransomware more often in comparison to APT groups. It was deduced that cybercrime groups prefer ransomware attacks as models such as RaaS(Ransomware as a Service) lowers the technical difficulties in generation of malware in comparison to other type of hacking activities, and ransomware attacks require less time investment to secure financial assets.
[Figure 2: Statistics of entities behind hacking activities using ransomware in 2023]
Targets of Hacking Groups Using Ransomware
Most hacking groups were found to have been using ransomware to secure financial profits. This section discusses about the countries, industries, and system affected by ransomwares in the year 2023.
1. Target Countries
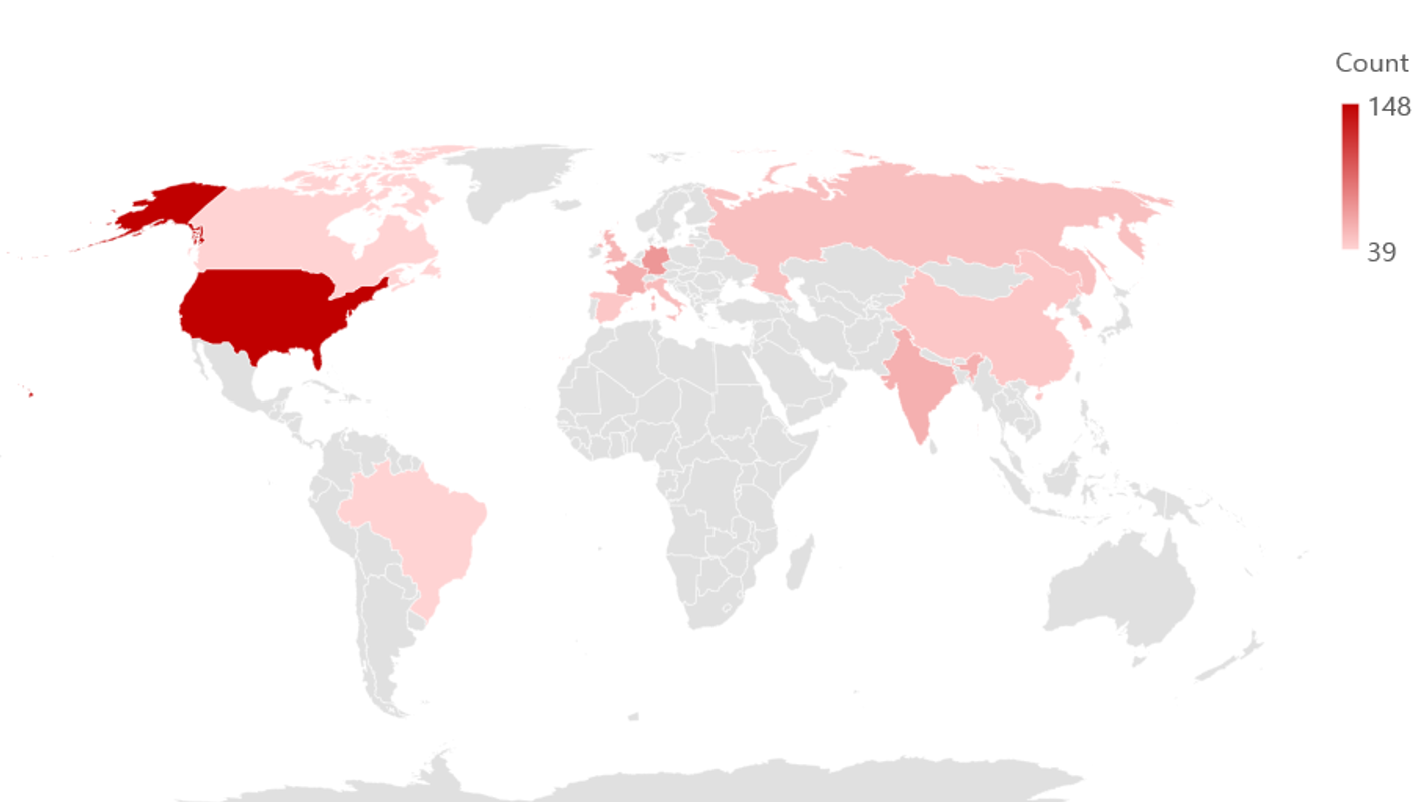
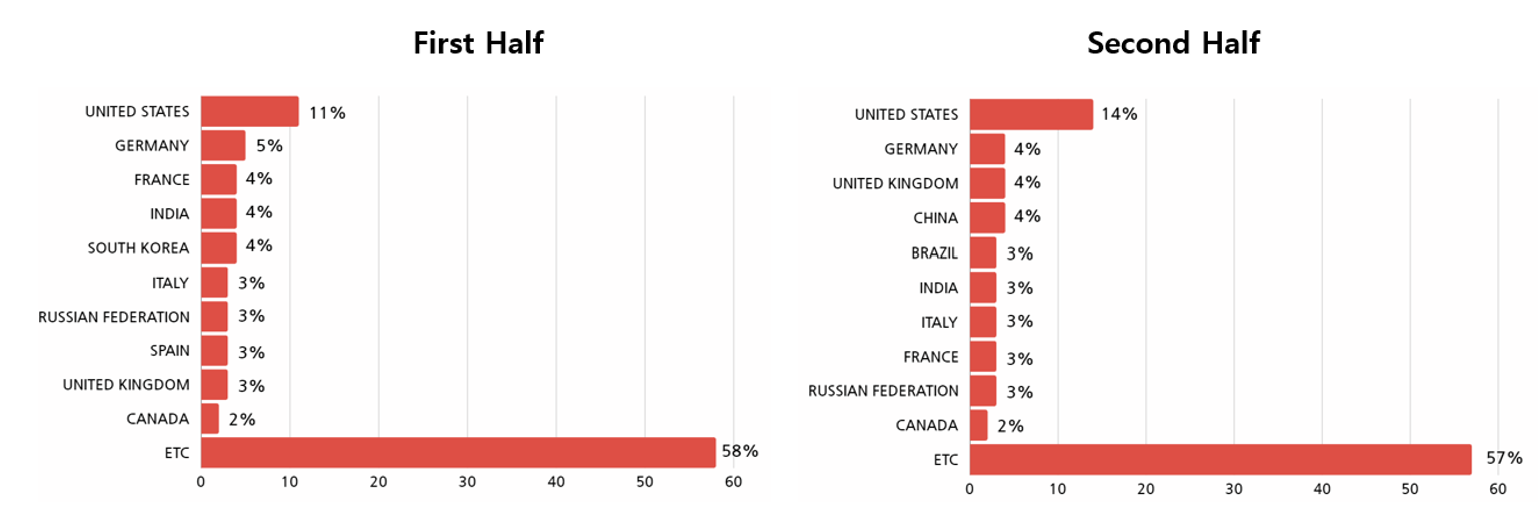
In 2023, majority of ransomware hacking activities were identified to have occurred in companies and institutions in Europe and North America, as countries in these continents were generally economically developed or emerging countries, and have the financial capabilities for paying the decryption costs. In both the first half and the second half of the year, the United States was found to have been the country where most number of ransomware attacks were targeted on.
[Figure 3: Target regions of ransomware hacking groups in 2023]
[Figure 4: Target countries of ransomware hacking groups in 2023]
2. Target Industries
Analysis of the industries of organizations and institutions affected by ransomware attacks carried out by hacking groups show that various industries were targeted in the first half of 2023, with the manufacturing industry having the highest number of attacks targeted on.
Manufacturing industry refers to the group of industries that produce products. When a ransomware attack occurs in this sector, disruptions may be caused in the operation of the product manufacturing factories. This results in temporary interruptions in product manufacturing, causing additional damage to suppliers and distributors of the products.
Given these circumstances, it is estimated that the manufacturing industry will have a high possibility of paying the decryption cost to recover the situation, considering the potential damage and financial loss caused by ransomware attacks.
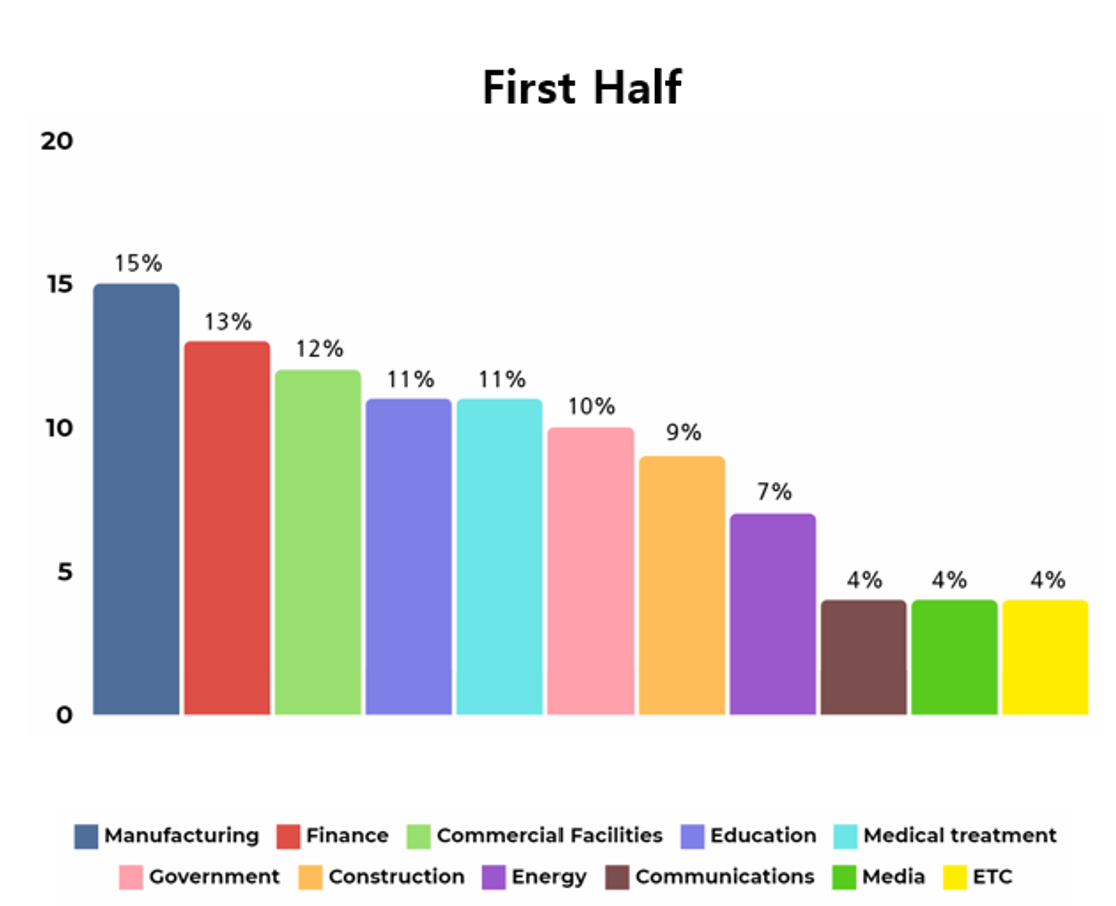
[Figure 5: Target industries of ransomware hacking groups in the first half of 2023]
Similar to the first half of the year, ransomware attacks were carried out against various industries in the second half of 2023, and the financial industry was found to have been targeted the most often, followed by manufacturing.
The financial industry includes not only companies that provide financial services such as banks and securities firms, but also finance-related companies such as investment and capital procurement.
When a ransomware attack occurs in the financial field, not only are the users of the financial service affected, but transaction partners and other parties involved are affected as well. Therefore, a significant scale of damage and financial losses could occur.
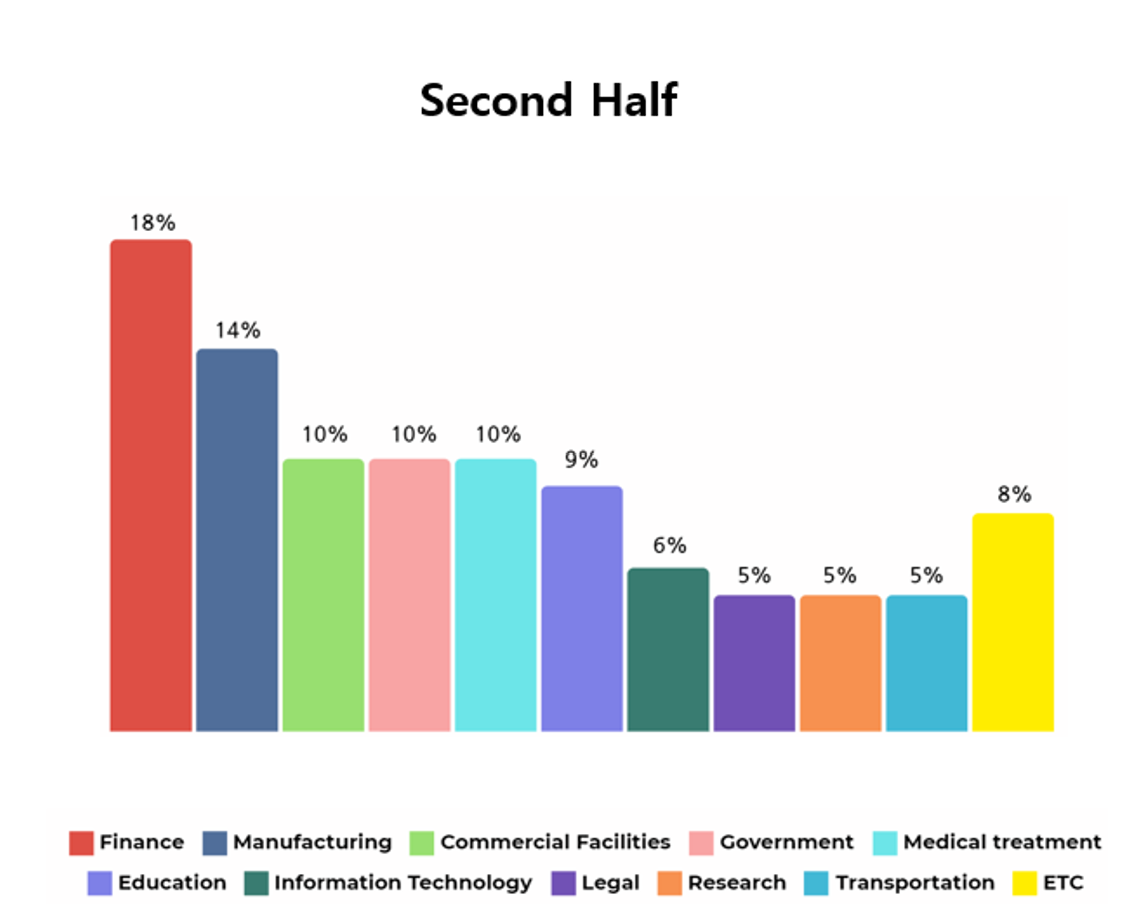
[Figure 6: Target industries of ransomware hacking groups in the second half of 2023]
As such, ransomware hacking groups were seen to have targeted on manufacturing and financial industries in the year 2023, which are prone to a larger scale of damage and financial losses. Other than the aforementioned industries, some of the targeted industries included commercial facilities, education and governments.
These industries were seen to have been targeted due to their higher risk of losses upon being attacked, such as service or educational operation disruptions, and would show a higher likelihood of paying ransom for file decryption.
3. Target Systems
According to the analysis of ransomware file types secured during the year 2023, the target systems for ransomware attacks were confirmed to be three: Windows, Linux, and macOS. Both in the first and second half of the year, it was shown that the most attacks were targeted on Windows systems.
Analysis of ransomware files acquired in the year 2023 shows that systems targeted by ransomware attacks were Windows, Linux, and macOS. For both first and second half of the year, most attacks were targeted on Windows systems.
Windows is the most commonly installed operating system on computers used by employees during work generally. From this perspective, ransomware operating on Windows OS could cause the most damage to businesses.
In addition, although the occurrence of ransomware attacks targeted on Linux operating systems were not common, attacks were carried out on servers being operated for special purposes such as Web Servers, File Server and Virtual Servers in organizations and institutions. Attacks against these Linux systems could lead to serious consequences such as business disruptions and the temporary suspension of services.
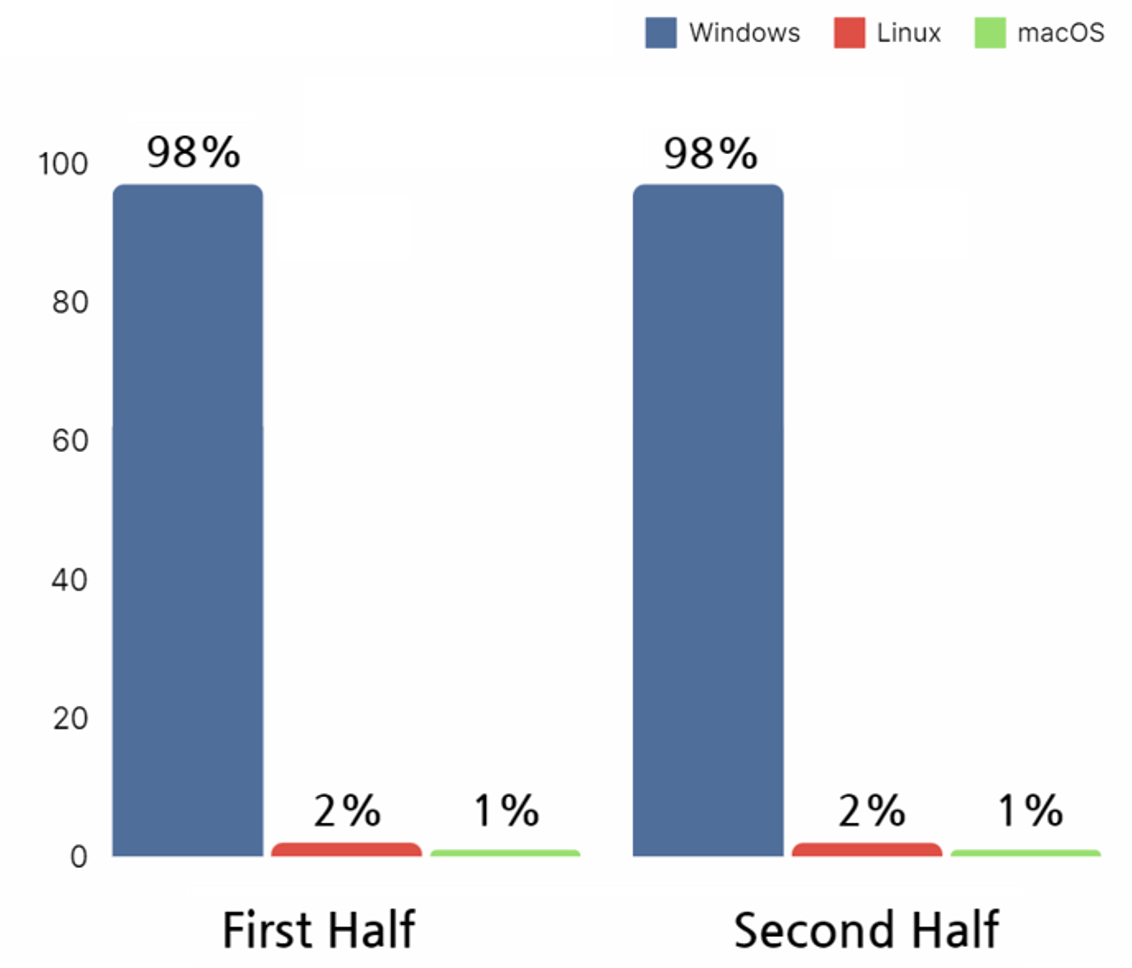
[Figure 7: Targeted systems of ransomware hacking groups in 2023]
Attack Techniques of Ransomware Hacking Groups
Ransomware hacking groups use various attack techniques to infiltrate target systems, encrypt data, and demand decryption costs from their victims. These techniques include exploiting vulnerabilities in systems, using open source and freeware tools, and other methods. This section describes the main attack techniques that have been identified to have been actively used by hacking groups during the year 2023.
1. Initial Access
The technique used by hacking groups to infiltrate target system in order to disseminate ransomware could be defined by the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix. NSHC Threat Research Lab analyses the techniques used by hacking groups to infiltrate target systems using the Initial Access Tactics under the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix, and results shows that the technique used most commonly by hacking groups for initial access were public-facing application exploitation and valid accounts.
In the first half of 2023, exploiting public-facing applications and valid accounts were seen as tactics used most commonly by the ransomware hacking groups during the initial access phase. Public-facing application exploitation is carried out by exploiting vulnerabilities identified from services such as web servers exposed in the internet and database servers, or by taking advantage of incorrect server configurations.
When a successful initial access is carried out using these methods, the hacking groups gain direct access to such servers, and infiltrating into company and institutional networks becomes relatively easier. As this method is difficult to be protected external security devices such as firewalls, an effective initial access can be carried out. In addition, acquiring access to internal network allows for additional system penetration and data stealing, making it easier to find other vulnerabilities within the system and increase the success rate of the attack.
Infiltration through valid accounts refer to the method of accessing using valid credential information obtained from the Dark Web and hacking forums. Security tools are unable to distinguish regular user behaviors from attackers using this method, so detection of the attack is difficult until the ransomware is executed. In addition, access to internal network connected to initially accessed system can be acquired, leading to more systems being infiltrated. This increases the likelihood of relatively critical data being encrypted.
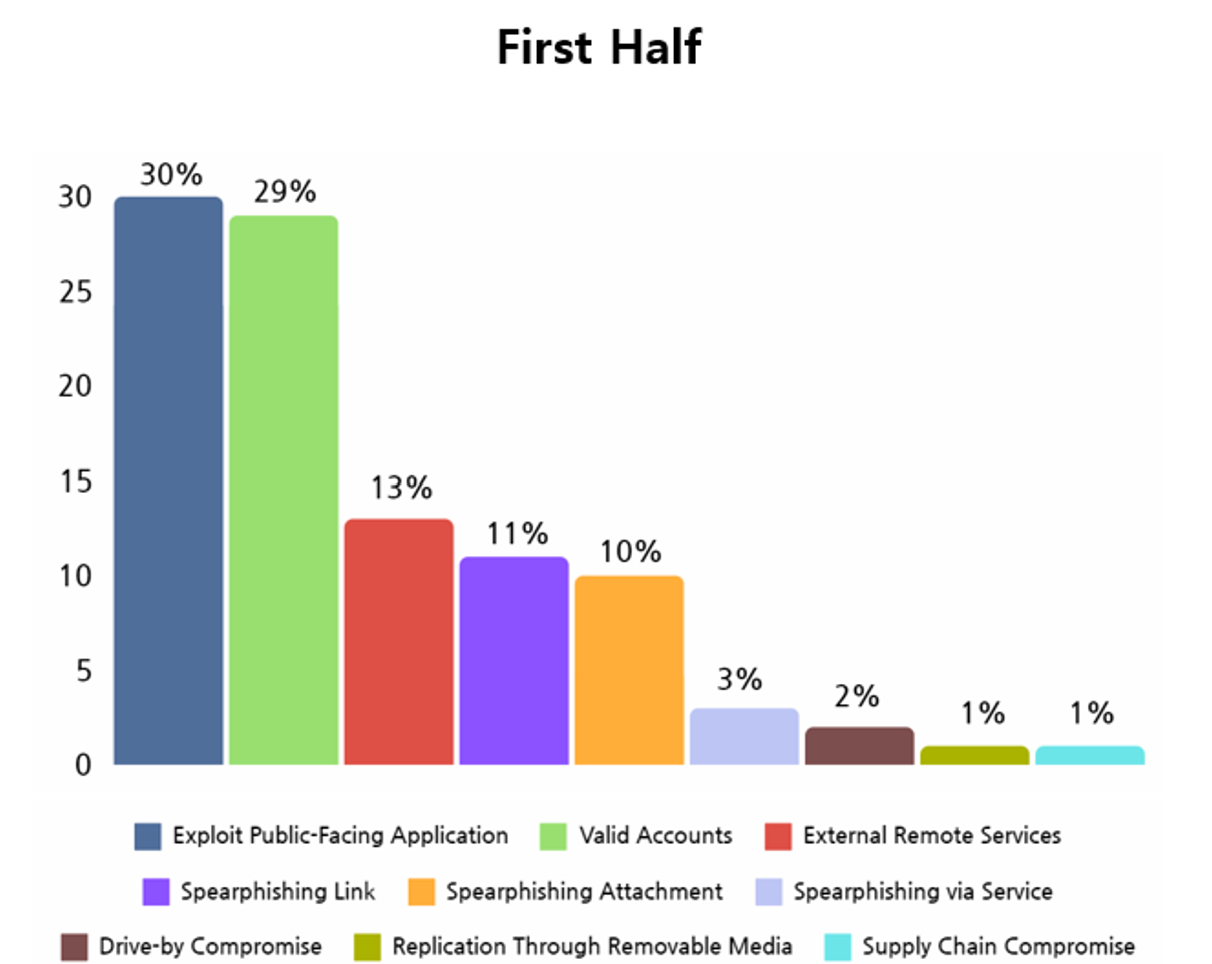
[Figure 8: Statistics of Initial Access methods used by ransomware hacking groups in first half of 2023]
In the second half of 2023, it was confirmed that the most commonly used methods for initial access were public-face application exploitation and valid accounts, similar to the first half of the year. In addition, the usage of external remote services technology has increased.
Such observations were seen as results of accelerations in transitions to cloud and SaaS(Software as a Service) which led to increases in security vulnerabilities in related infrastructures. Hacking groups can easily access computers used for business purposes in external networks of companies and organizations using remote services, as they are relatively more vulnerable compared to systems in internal networks. Once they successfully penetrate, they can expand their attacks to the entire internal network, making the use of remote service technology a growing concern.
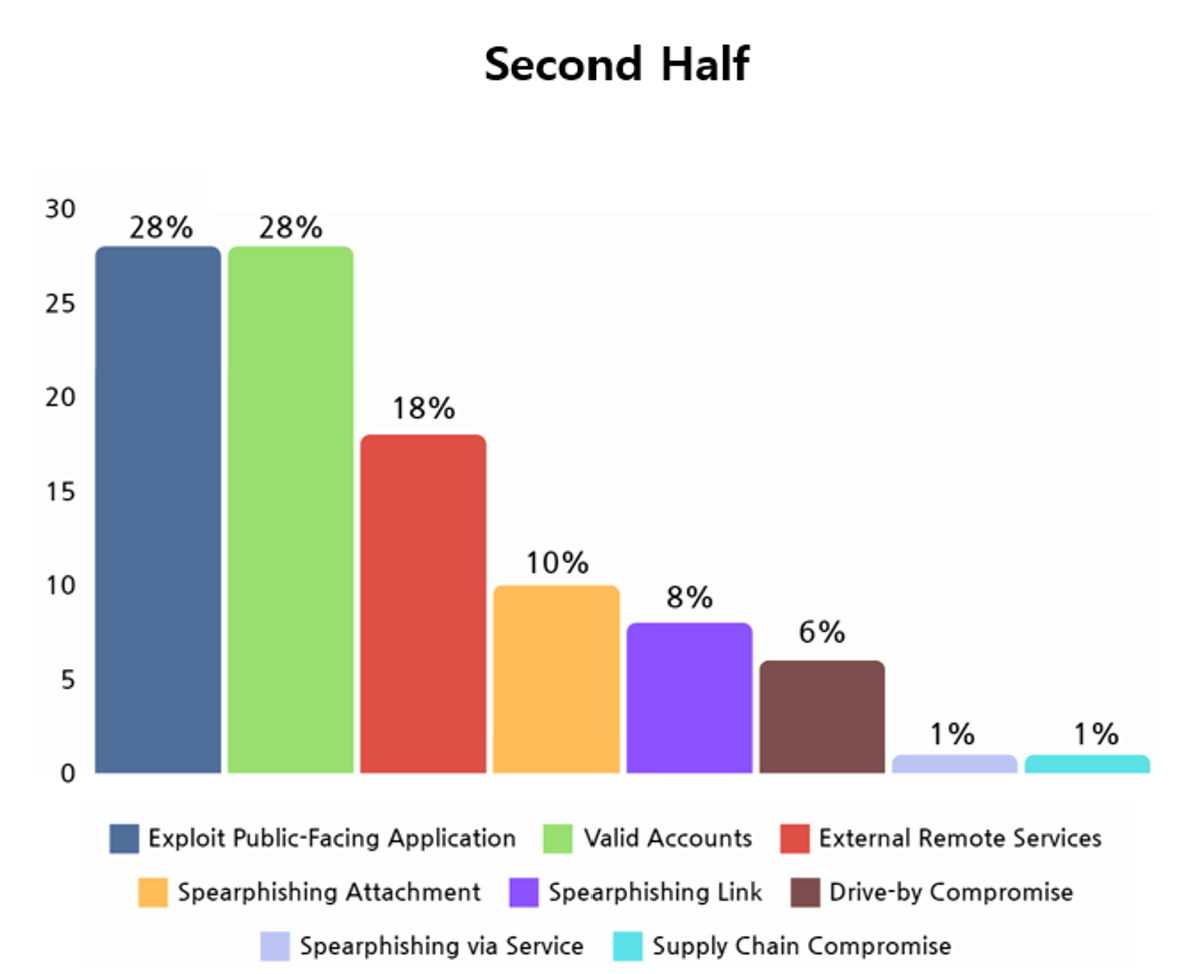
[Figure 9: First infiltration method of ransomware hacking groups in the second half of 2023]
2. Vulnerability
Ransomware hacking groups exploit various vulnerabilities to carry out hacking activities. Various commercial or open-source exploit kits that could automatically attack vulnerabilities in systems exist in the online space, and ransomware hacking groups prefer to use such tools to minimize resources used for ransomware dissemination. This section describes the main vulnerabilities exploited by the ransomware hacking groups in the year 2023.
Analysis of the top 10 vulnerabilities that were most commonly exploited by ransomware hacking groups in 2023 shows that the following three were utilized the most in the year.
- CVE-2021-21974: VMware ESXi Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
- CVE-2023-27350: PaperCut MF/NG Improper Access Control Vulnerability
- CVE-2021-27876: Veritas Backup Exec Agent File Access Vulnerability
CVE-2021-21974 is the remote code execution vulnerability of VMware ESXi. This vulnerability allows attackers to execute malware in remote settings, and could be used in spreading malware by controlling the ESXi server.
CVE-2023-27350 is a vulnerability in PaperCut MF/NG that allows unauthorized users to access the system. This vulnerability can be exploited by attackers to access sensitive data or install ransomware on the system.
CVE-2021-27876 is a vulnerability in Veritas Backup Exec Agent that allows an attacker to gain unauthorized access to the file system. This vulnerability can be used by an attacker to encrypt or delete backup data, maximizing the impact of a ransomware attack.
Analysis of vulnerabilities exploited in first half of the year shows that RCE (Remote Code Execution) was the most commonly exploited vulnerability. RCE vulnerability allows malicious commands to be executed remotely on software or products affected by the vulnerability. In addition, the vulnerable software used is mostly identified as applications classified as servers. When attacking by exploiting vulnerabilities on the server, the attacker can not only secure persistence and evade detection, but also gain access to sensitive data and perform lateral movement to adjacent systems or other network ranges, potentially causing the damage to spread. To exploit these characteristics, attackers are mainly known to target servers by exploiting vulnerabilities.
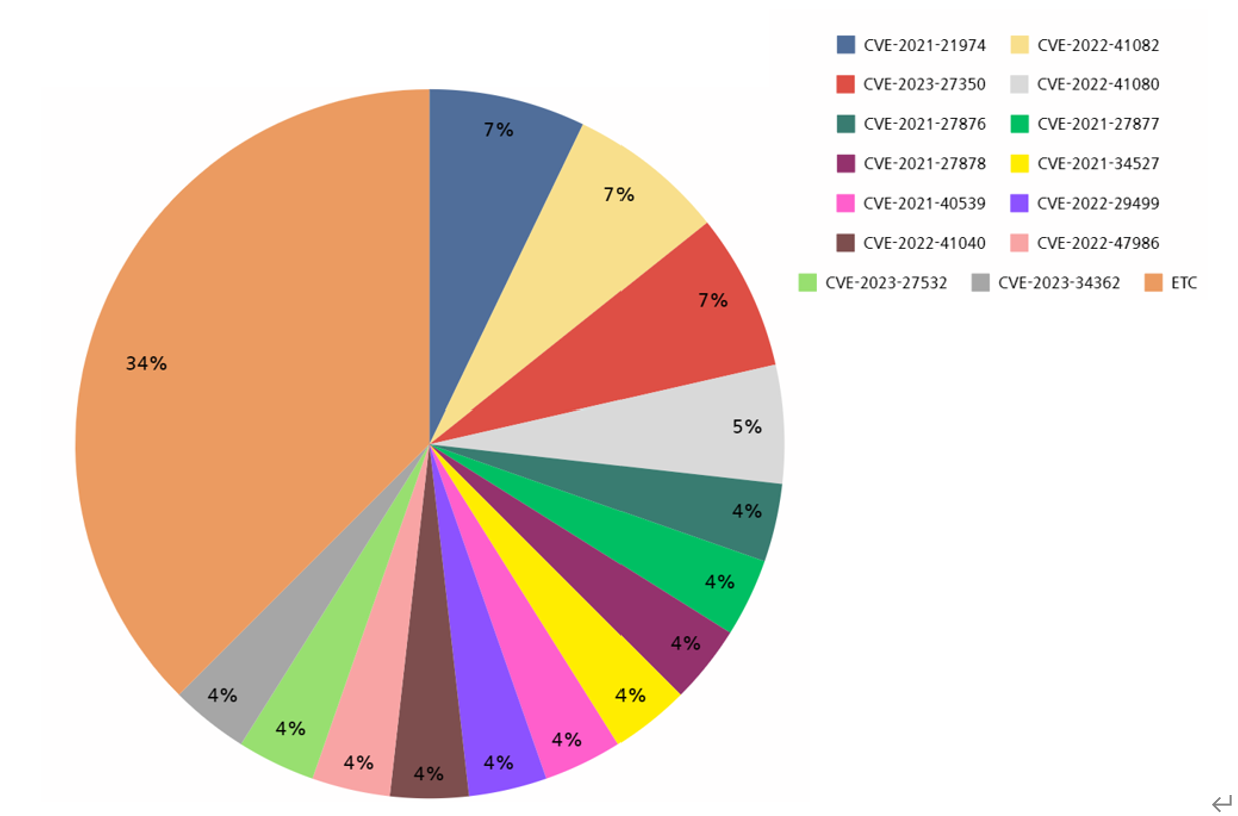
[Figure 10: Vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware hacking groups in the first half of 2023]
|
Vulnerability |
Classification | Target |
|
CVE-2021-21974 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
VMware ESXi OpenSLP Services |
|
CVE-2022-41082 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Microsoft Exchange Server |
|
CVE-2023-27350 |
Improper Access Control Vulnerability |
PaperCut MF/NG Improper |
|
CVE-2022-41080 |
Privilege Escalation Vulnerability |
Microsoft Exchange Server |
|
CVE-2021-27876 |
File Access Vulnerability |
Veritas Backup Exec Agent |
|
CVE-2021-27877 |
Improper Authentication Vulnerability |
Veritas Backup Exec Agent |
|
CVE-2021-27878 |
Command Execution Vulnerability |
Veritas Backup Exec Agent |
|
CVE-2021-34527 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Microsoft Windows Print Spooler |
|
CVE-2021-40539 |
Authentication Bypass Vulnerability |
Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus |
| CVE-2022-29499 | Data Validation Vulnerability |
Mitel MiVoice Connect |
[Table 1: Vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware hacking groups in the first half of 2023]
Analyzing the top 10 vulnerabilities exploited in the second half of 2023 revealed that the most exploited vulnerability was “CVE-2020-1472”. This vulnerability is a privilege escalation vulnerability in “Microsoft Netlogon”, which manages the security channel connecting computers and domain controllers (DC) on Windows Server. A privilege escalation vulnerability refers to a vulnerability that allows an attacker to gain system privileges and perform various malicious activities at the same level as system privileges.
According to the analysis of vulnerability types utilized in the second half of the year, Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities (RCE) were heavily exploited and the targeted software for these vulnerabilities was mostly classified as server applications, similar to the first half of the year. In particular, VPN (Virtual Private Network) related software such as “Fortinet FortiOS SSL VPN” was seen to have been heavily exploited in the second half. This is believed to be an attempt by hacking groups to expand the scope of ransomware attacks by targeting a wider range of software compared to the first half of the year.
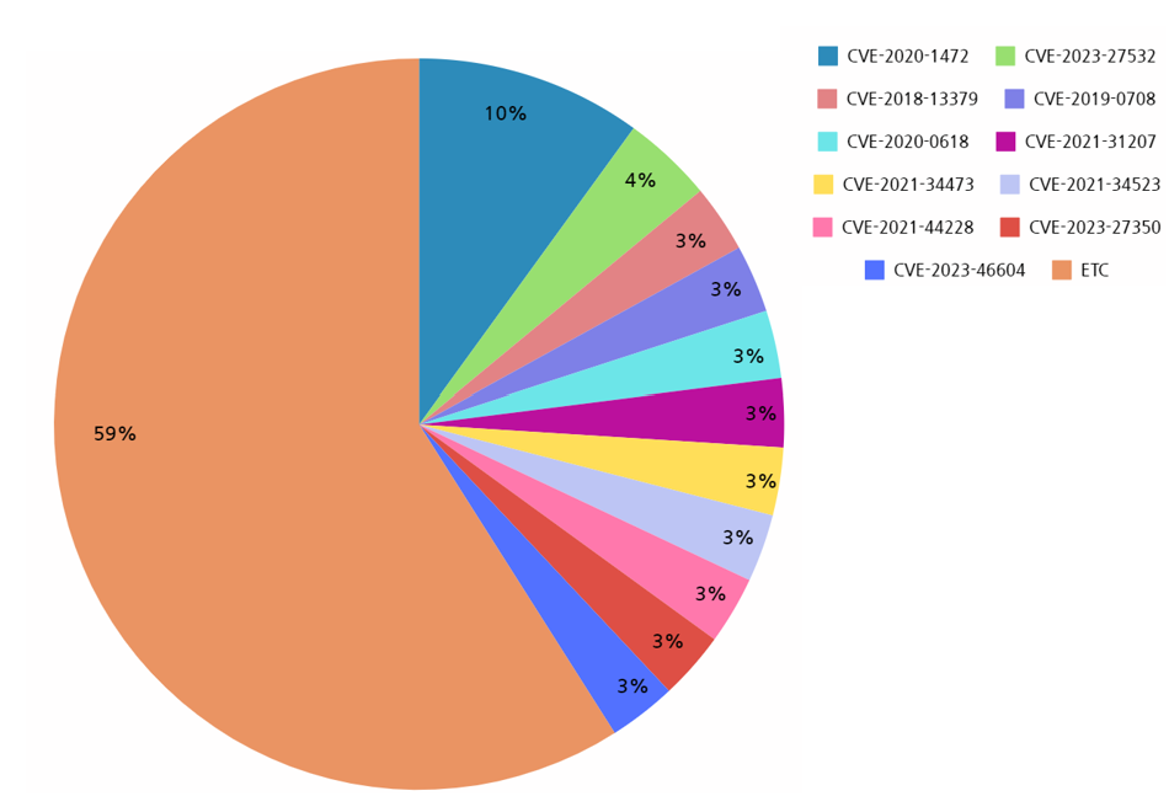
[Figure 11: Vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware hacking groups in the second half of 2023]
|
Vulnerability |
Classification |
Target |
|
CVE-2020-1472 |
Privilege Escalation Vulnerability |
Microsoft Netlogon |
|
CVE-2023-27532 |
Missing Authentication for Critical Function Vulnerability |
Veeam Backup & Replication Cloud Connect |
|
CVE-2018-13379 |
Path Traversal Vulnerability |
Fortinet FortiOS SSL VPN |
|
CVE-2019-0708 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Microsoft Remote Desktop Services |
|
CVE-2020-0618 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services |
|
CVE-2021-31207 |
Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Microsoft Exchange Server |
|
CVE-2021-34473 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Microsoft Exchange Server |
|
CVE-2021-34523 |
Privilege Escalation Vulnerability |
Microsoft Exchange Server |
|
CVE-2021-44228 |
Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Apache Log4j2 |
|
CVE-2023-27350 |
Improper Access Control Vulnerability |
PaperCut MF/NG |
|
CVE-2023-46604 |
Deserialization of Untrusted Data Vulnerability |
Apache ActiveMQ |
[Table 2: Vulnerabilities exploited by ransomware hacking groups in the second half of 2023]
3. Open Source and Freeware Tools
Hacking groups take advantage of open-source and freeware as their attack tools. Open-source and freeware refer to commercial tools or tools that have released their source code for free, and are also utilized by general users as needed.
Hacking groups were seen to have been using open-source and freeware tools to bypass detection of security solutions while moving within the targeted organization and spreading the ransomware.
Analysis of the top 10 open-source and freeware tools used by ransomware hacking groups in the first half of 2023 shows that Remote Administrator Software was most frequently exploited.
Remote control program refers to a program that can connect to a host through an authentication process from the client. Hacking groups were deduced to have used remote control tools to remotely control targeted systems as attacks performed through a remote-control program go through an intermediary server, making it difficult to distinguish between legitimate traffic from normal users and malicious traffic from attackers.
Analyzing the Top 10 open source and freeware tools in the first half of 2023 showed that AnyDesk was the most widely used remote control program, followed by Mimikatz, a Windows credential collection tool, and Rclone.
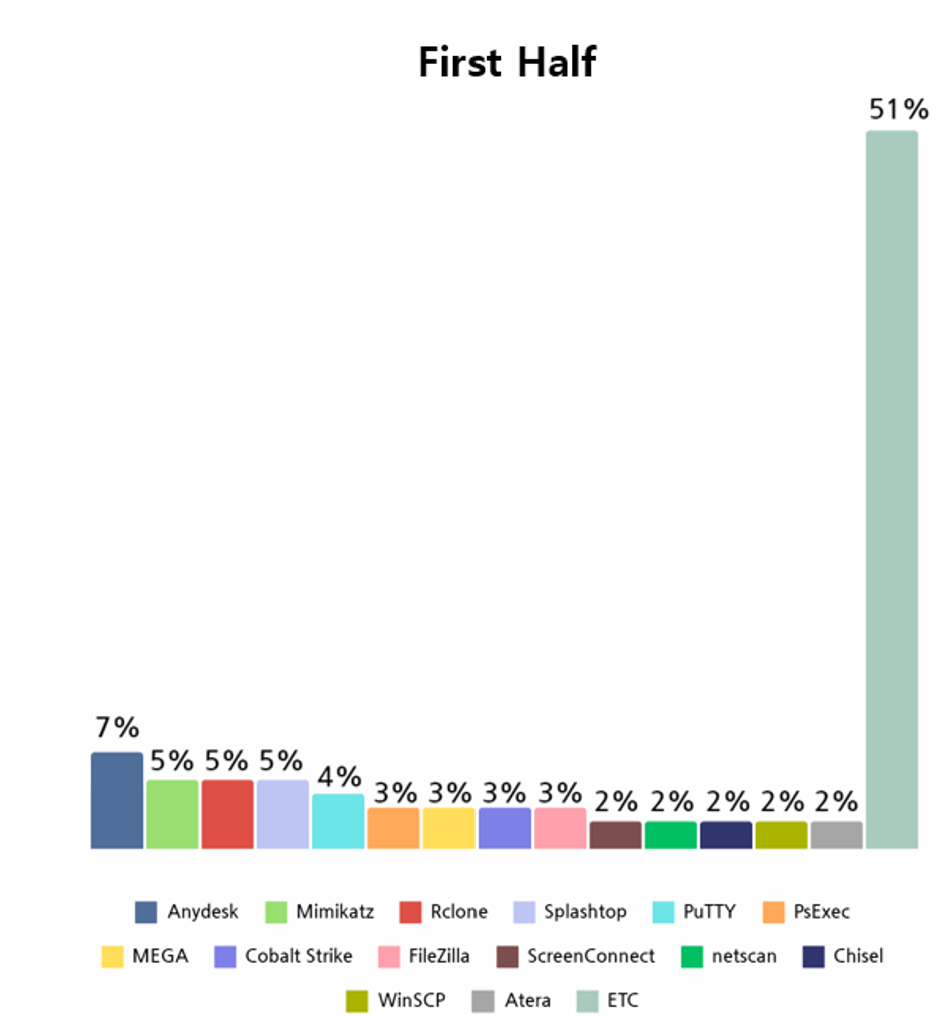
[Figure 12: Open source and freeware tools used by ransomware hacking groups in the first half of 2023]
|
Tool |
Tool Function |
|
AnyDesk |
Remote control program |
|
Mimikatz |
Windows credential information collection tool |
|
Rclone |
Cloud storage file management program |
|
Splashtop |
Remote control program |
|
PuTTY |
Remote control program |
|
PsExec |
Remote execution program |
|
MEGA |
Cloud storage service |
|
Cobalt Strike |
Penetration testing tool |
|
FileZilla |
File transfer program |
|
AdFind |
Windows Active Directory information collection tool |
[Table 3: Open-source and freeware tools used by ransomware hacking groups in the first half of 2023]
Ransomware hacking groups exploited AnyDesk to remotely execute malware in the targeted system. AnyDesk offers a “Unattended Access” feature, which allows hacking groups to remotely control target systems without additional permission by entering a pre-set password.

[Figure 13: AnyDesk’s unattended access setting screen]
Mimikatz is a Windows credential collection tool. Through this tool, hacking groups using ransomware can obtain administrator privileges to execute ransomware and spread attacks to other systems using the collected account information.
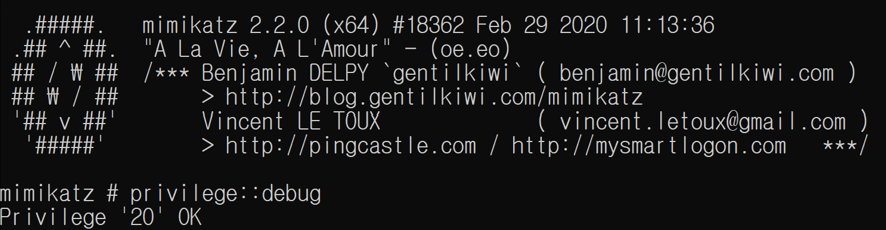
[Figure 14: Mimikatz Execution Screen]
Rclone is a program that can manage files targeting more than 70 cloud storage services. It is believed to have been used in the process of stealing original data before encrypting them with ransomware, using both free and commercial cloud services.

[Figure 15: Homepage screen of Rclone]
[Figure 16: Part of the storage supported in Rclone]
Cobalt Strike, a pentesting tool, was the most utilized tool in the second half of 2023. Cobalt Strike has the characteristics of being able to generate beacon format malware, which carries out command control functions, without the need for complex coding knowledge required in creating malware. This tool is a commercially available penetration testing program, but it is possible to find cracked versions or code that can be built through GitHub and other forums.
Cobalt Strike supports various attack functions such as initial infiltration and lateral movement, which can reduce the number of attack tools used until the hacking attack is ultimately terminated. Less tools being required in ransomware attacks means that resources used in attacks such as time occupied in the attack system could be reduced, thus Cobalt Strike became the most preferred tool among hacking groups.
[Figure 17: Cobalt Strike Shellcode Generator]
Similar to the first half of the year, Mimikatz, a credential collection tool, and PsExec and AnyDesk, which could remotely control targeted systems, were seen to have been widely used in the second half of the year as well. These open source and freeware tools were deduced to have been used to obtain the authority to execute ransomware on the target system or to propagate their target system.
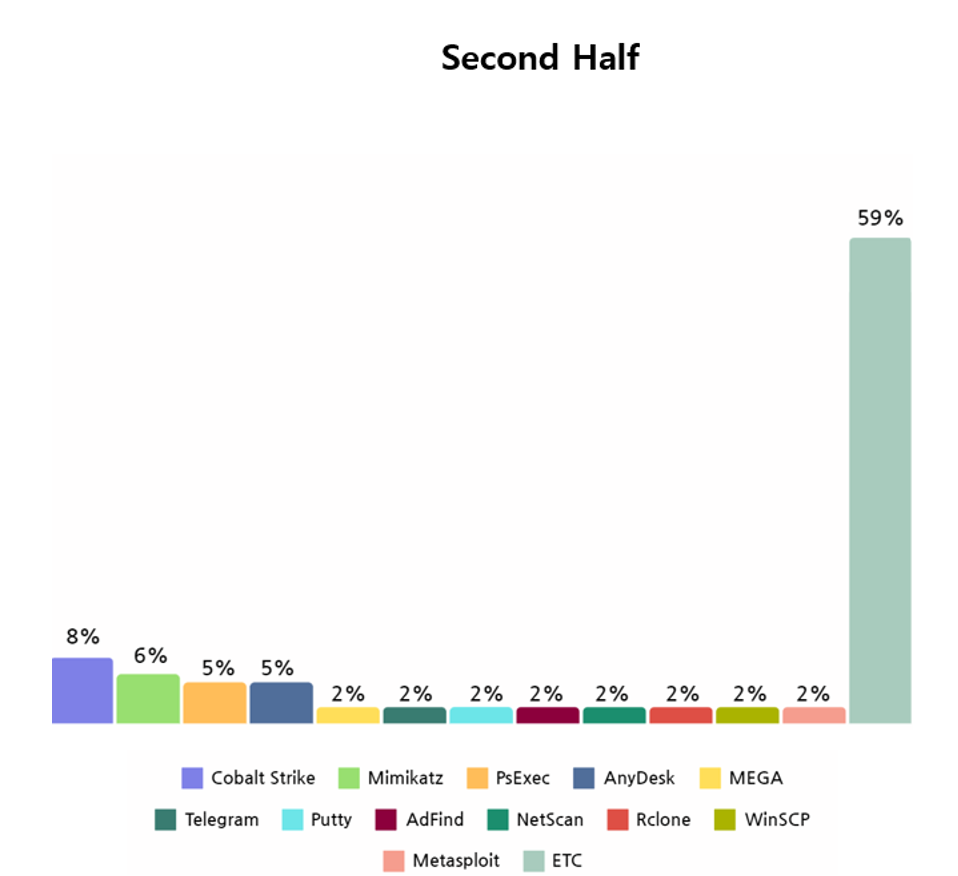
[Figure 18: Open source and freeware used by ransomware hacking groups in second half of 2023]
|
Tool |
Function |
|
Cobalt Strike |
Penetration testing tool |
|
Mimikatz |
Windows Credential information collection tool |
|
PsExec |
Remote execution program |
|
AnyDesk |
Remote control program |
|
MEGA |
Cloud storage service |
|
Telegram |
Messenger |
|
Putty |
Remote control program |
|
AdFind |
Window Active Directory information collection tool |
|
NetScan |
Network scanner |
|
Rclone |
Cloud storage file management program |
|
WinSCP |
File transfer program |
|
Metasploit |
Penetration testing tool |
[Table 4: Open source and freeware tool used by ransomware hacking groups in second half of 2023]
Infrastructure of Ransomware Hacking Groups
When a ransomware detects that the data in the targeted organization has been encrypted, a ransom note indicating the method for paying monetary benefits to the ransomware hacking groups is generated. Generally, ransom notes generated by ransomware contains infrastructure information such as point of contact with the ransomware hacking groups or the cryptocurrency wallet address to receive crypto payments.
This section identifies network information used by ransomware hacking groups in managing their attack history and financial information used in receiving decryption payments as infrastructure. Infrastructure could be classified into three types, the .onion domain, email, and social media platform. Ransomware hacking groups were found to have utilized onion domains the most.
Onion domains refer to anonymous website addresses that can only be accessed through the Tor network. Attackers are difficult to be traced back to when using the Tor network, thus being the most heavily utilized infrastructure of the hacking groups in 2023.
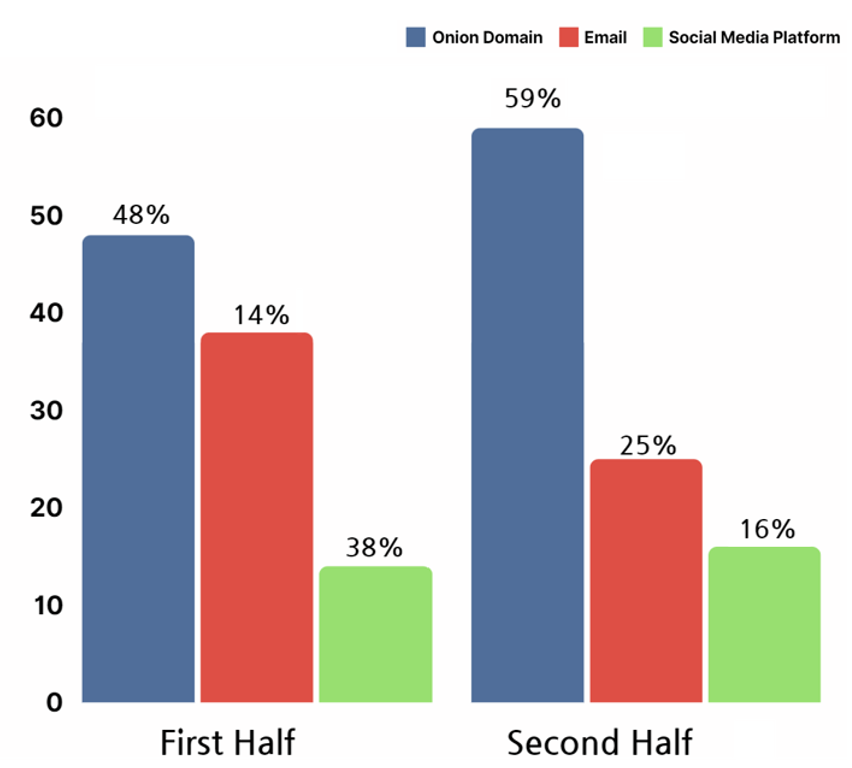
[Figure 19: Infrastructure of ransomware hacking groups]
1. Onion Domain Operation Format
Onion domains were generally used during communication with the victims or to post stolen data. In the first half of the year, onion domains were commonly used with the purpose of posting data leaks, but in the second half of the year, there were more hacking groups operating as a closed circle.
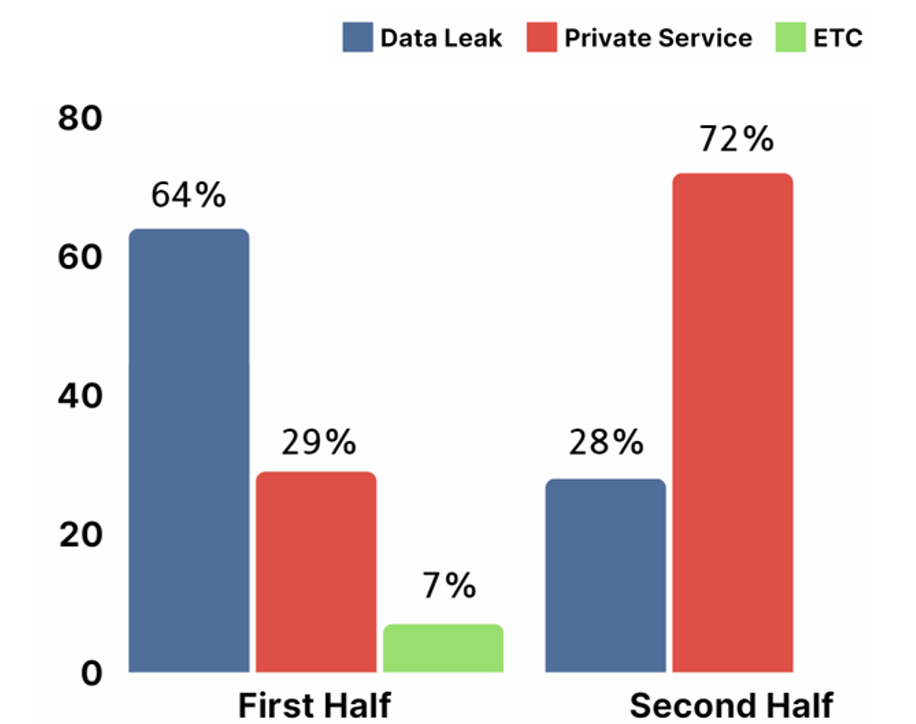
[Figure 20: Format of Onion domain operation of ransomware hacking groups in first half of 2023]
In the first half of 2023, onion domains were utilized the most often with the purpose of publishing data stolen from targeted systems or posting a list of victimized companies. Hacking groups publicly disclosed some of the data such as filenames and file paths from the target system to prove the authenticity of the leaked data, and even posted links to compressed files containing the stolen data through file sharing sites. Additionally, they pressurized the targets by indicating a deadline for monetary transactions, urging the victims to pay the recovery fees.
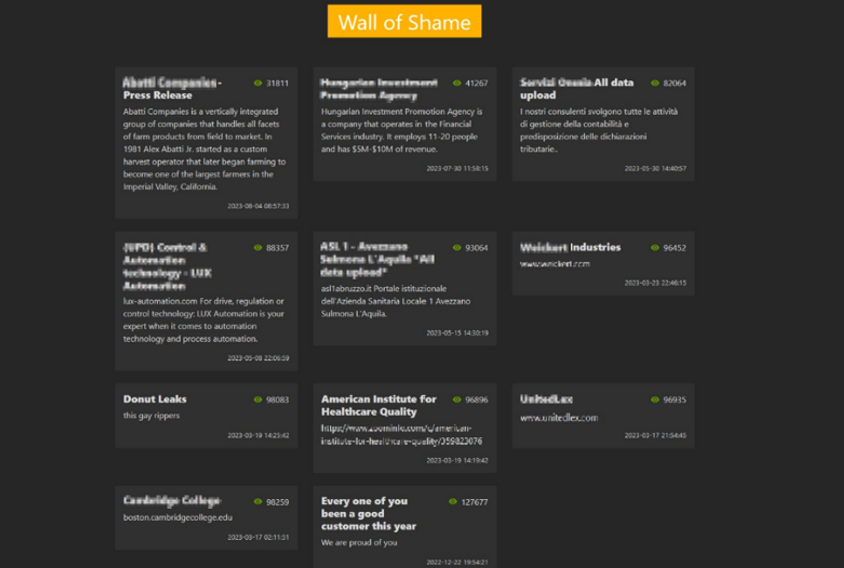
[Figure 21: A case of Onion domain operated to display the list of affected corporates]
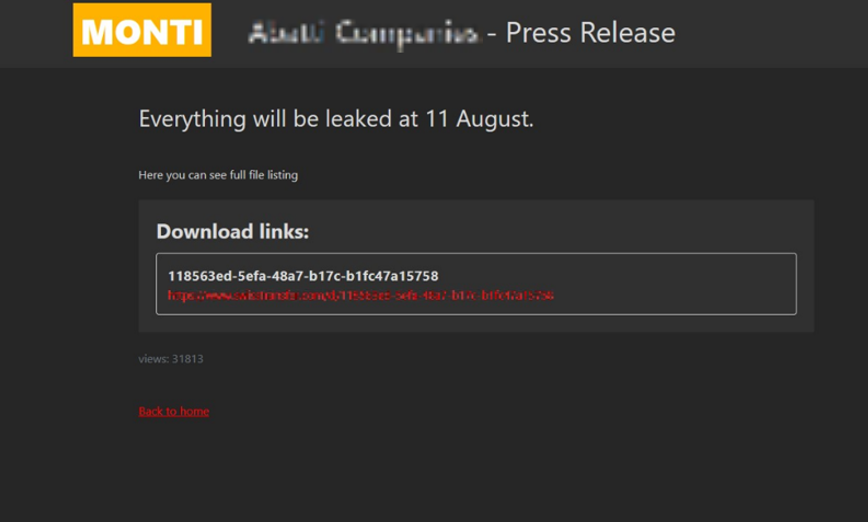
[Figure 22: A case of Onion domain operated with the aim of displaying list of affected organizations]
Analysis of Onion domains identified in the second half of 2023 showed that many onion domains were operated in a closed form that can only be accessed through a specific authentication process. This report refers to these websites as Private Services.
[Figure 23: An example of Onion domain being operated as a private service]
Private Service is operated in a form that can only be accessed through a separate authentication process. It could be used for communication between victim and the hacking groups after a ransomware attack, or as a forum for selling attack techniques, tools, or stolen data.
2. Email Domain Address
There are cases where ransomware hacking groups notify the victims of the ransomware decryption process through emails.
Various email domains were in use throughout the year of 2023, and the onion mail domain was found to be the most preferred domain address.
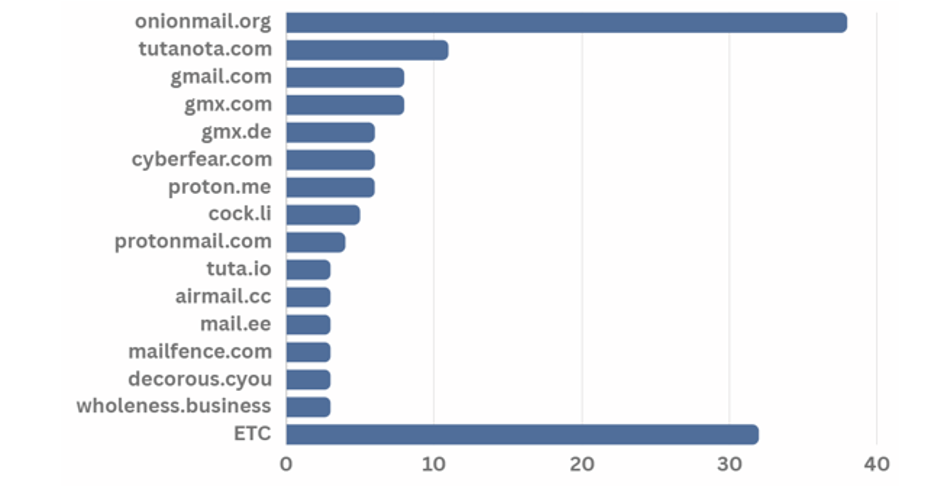
[Figure 24: Email domain used by ransomware hacking groups in first half of 2023]
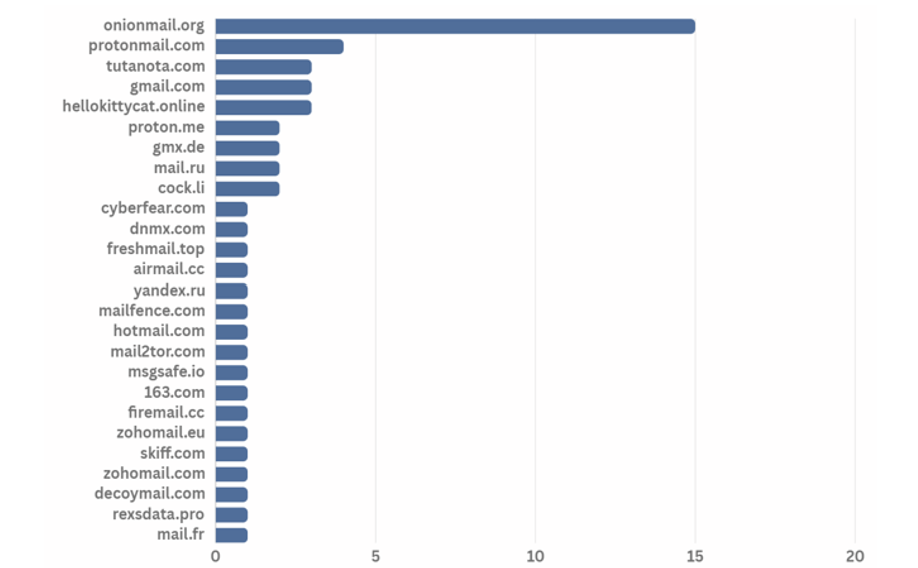
[Figure 25: Email domain used by ransomware hacking groups in second half of 2023]
Onion Mail domain is an email server used in the Tor browser. It is encrypted using the PGP public key, just like the Onion domain, and thus is anonymous. In addition, hacking groups are known to prefer and use Onion Mail domains because they do not require separate authentication procedures such as personal information. The service provides three email account domains, “onionmail.org”, “onionmail.com”, and “[random string].onion”.
[Figure 26: Homepage of Onion Mail]
[Figure 27: Account generation page in Onion Mail]
3. Social Media Platform
In the first half of 2023, there were many ransomware hacking groups using Tox, an encrypted messenger application, but Telegram was found to be more dominant in the second half of the year.
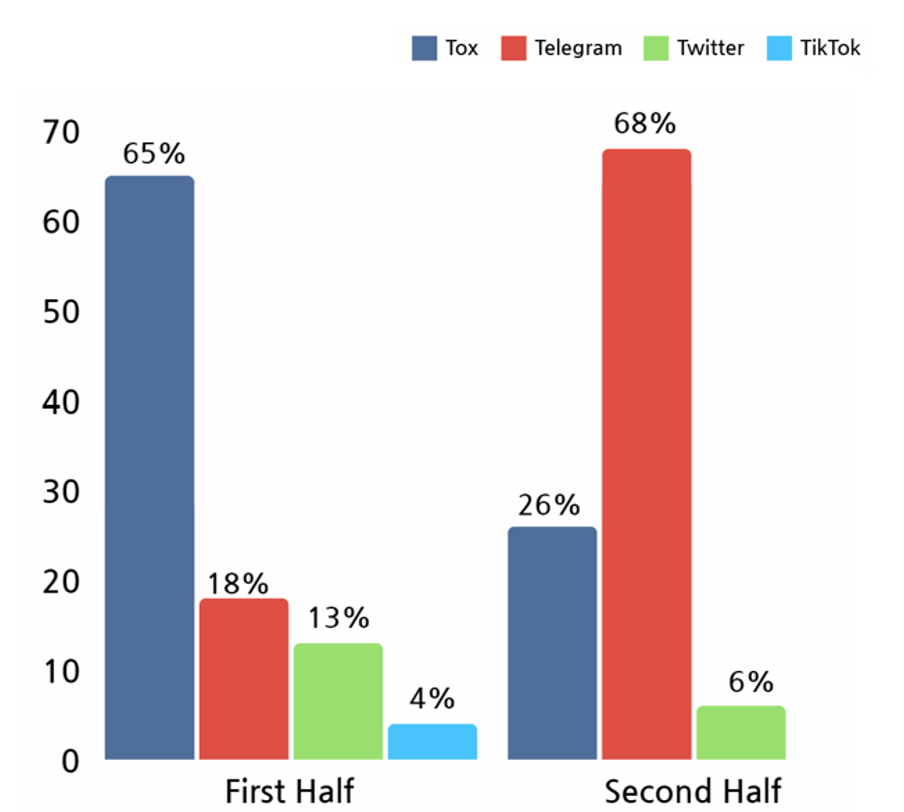
[Figure 28: Social media platform used by ransomware hacking groups in 2023]
Tox is a messenger service that can be used without personal information authentication such as phone numbers and email addresses. In the first half of 2023, hacking groups that attempted to contact their targets through Tox were found to have been more active.
[Figure 29: Execution screen of Tox, an encrypted messenger]
In the second half of the year, Telegram was found to be more widely used. Telegram supports various functions through its API (Application Programming Interface), so hacking groups using ransomware can use Telegram channels as C2 (Command and Control) servers, making it easier to send original data before encrypting information or data from targeted systems that have been affected by ransomware attacks.
4. Cryptocurrency
The main purpose of ransomware dissemination is to acquire financial resources. Ransomware hacking groups decided on cryptocurrency, which is encrypted using blockchain technology, as the means to receiving financial gains.
Cryptocurrency transaction occurs through data known as cryptocurrency wallet addresses instead of traditional account numbers. The transaction history can be viewed, but the lack of a central controlling institution or organization makes tracking of the owner difficult, guaranteeing anonymity. Due to the anonymity and difficulty of tracking, hacking groups are believed to prefer receiving decryption costs in cryptocurrency. Analysis of cryptocurrency symbol types in the year 2023 shows that Bitcoin (BTC) was used to receive the ransom throughout the year.
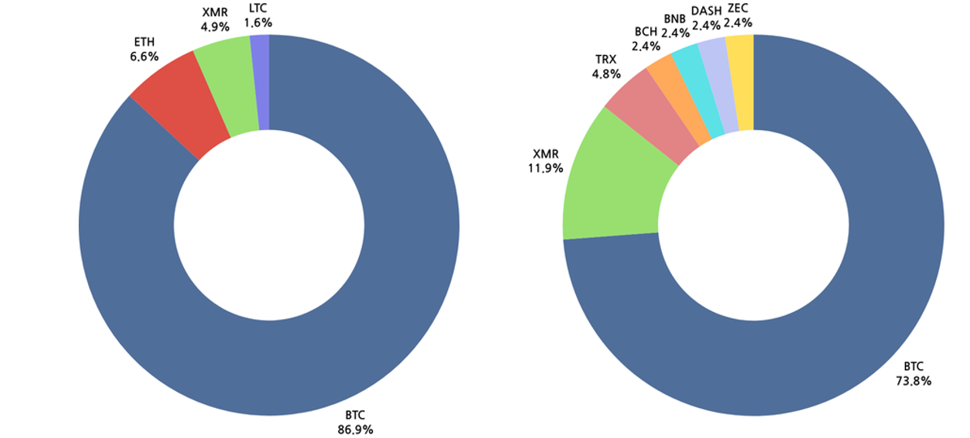
[Figure 30: Cryptocurrency wallet address symbol of ransomware hacking groups in 2023]
According to data released by CoinMarketCap, which shares cryptocurrency prices and trading information, the value of Bitcoin has been continuously rising since 2023. Therefore, ransomware hacking groups have chosen Bitcoin as their means of transaction due to its consistent increase in value and stability.
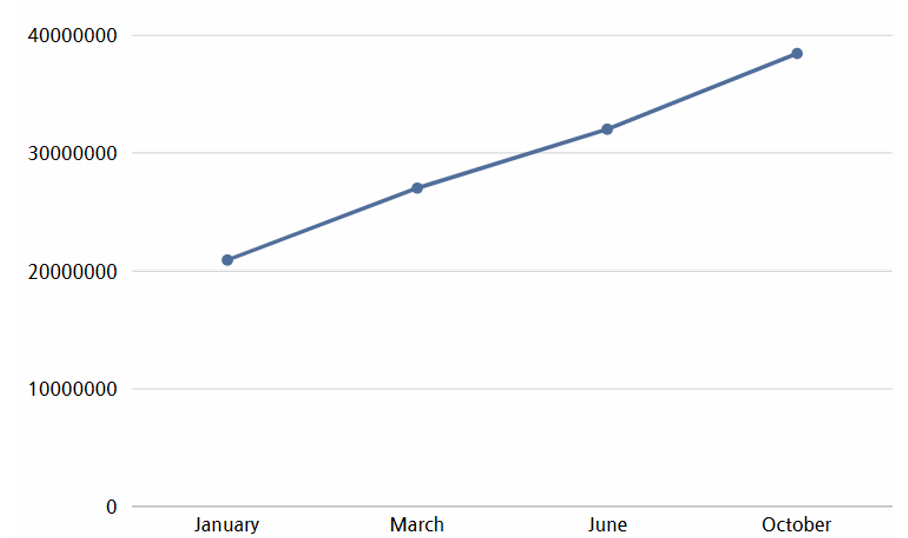
[Figure 31: 2023 Bitcoin price trend]
(Source: CoinMarketCap, https://economist.co.kr/article/view/ecn202401030017)
In the second half of the year, they chose a variety of cryptocurrencies as ransom payment methods compared to the first half of the year. The types of cryptocurrencies they used as ransom payment methods in the second half of the year are as follows.
|
Cryptocurrency |
Symbol |
Characteristics |
|
Bitcoin |
BTC |
Most widely known and has the longest history, operated without the involvement of a central organization |
|
Monero |
XMR |
Emphasizes privacy and anonymity, conceals transaction records and ownership |
|
TRON |
TRX |
Based on a decentralized content sharing platform, focused on efficiently distributing and sharing content |
|
Bitcoin Cash |
BCH |
Faster transaction speed in comparison to bitcoin, expanded the size of blocks used in transaction processing |
|
Binance Coin |
BNB |
Used in Binance exchanges, regularly discards some of the coins to maintain rarity |
|
Dash Coin |
DASH |
High transaction speed, conceals transaction history and value |
| Zcash | ZEC |
Protects transaction details using zero-knowledge cryptography |
[Figure 4: Types of cryptocurrencies utilized in second half of 2023]
Conclusion
This report describes the various attack techniques, tools, infrastructure information and case studies of ransomware hacking groups in the second half of the year 2023. As seen in cases of ransomware incidents, attacks using ransomware are occurring continuously. This may result in critical damages such as disruptions in services and data leaks for companies and organizations. To prevent such incidents, a response system based on data related to ransomware hacking attacks is necessary. An active response system should be established by acquiring cyber threat intelligence that can provide information on attack techniques and tools used by hacking groups, and utilizing data on attacks and recent attack techniques.
The full report detailing each event together with IoCs (Indicators of Compromise) and recommendations is available to existing NSHC ThreatRecon customers. For more information, please contact service@nshc.net.
